When it comes to optical test and measurement instruments, one vital component often plays a pivotal role – beamsplitters. These unassuming optical devices are indispensable for various reasons, offering versatility and cost-effectiveness that have made them a favorite among optical engineers and scientists. In today’s post, we’ll explore the applications of beamsplitters in the world of optical testing and measurement.
What Are Beamsplitters and Why Are They Important?
Beamsplitters are optical devices designed to perform three primary functions:
Splitting Light Beams: Beamsplitters are adept at dividing a single beam of light into two or more separate beams. This functionality serves various optical testing and measurement purposes, including interferometry, spectroscopy, and microscopy.
Recombining Light Beams: They can also recombine multiple beams of light. This feature is particularly useful for measuring the phase difference between these beams, a crucial aspect of interferometry.
Controlling Light Intensity: Beamsplitters are instrumental in adjusting the intensity of a light beam, which is essential for optical power measurement and beam attenuation.
Versatility in Optical Test and Measurement
Beamsplitters are integral components in many optical test and measurement instruments, primarily because of their versatility and ease of use. They have found their place in a range of applications:
Interferometers: Beamsplitters are a key part in interferometers. They divide a light beam into two or more beams, recombine them, and the result is an interference pattern. This pattern can be used to gauge a material’s refractive index, thin film thickness, or surface properties of optical components.
Spectrometers: In spectrometers, beamsplitters come into play by splitting a light beam into its component wavelengths. This information is invaluable for identifying the elements present in a sample or measuring the concentration of substances in a solution.
Microscopes: Some microscopes use beamsplitters to split a beam of light into multiple beams, which are subsequently recombined to create a three-dimensional image of the sample. This enables researchers to gain a deeper insight into the microscopic world.
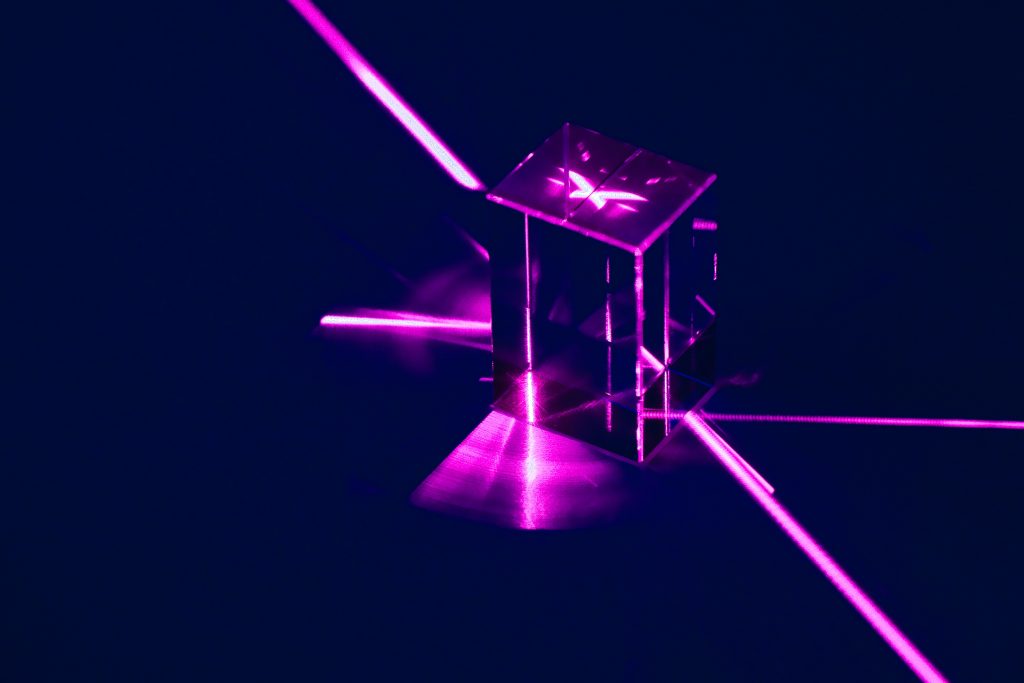

Optical Power Meters: Beamsplitters find application in optical power meters, where they are used to measure the intensity of a light beam. This measurement is crucial for ensuring that light sources deliver the correct power and for quantifying losses in optical systems.
Optical Attenuators: Beamsplitters can also be employed to create optical attenuators, which reduce the intensity of a light beam. These attenuators serve various purposes, including safeguarding optical components from damage and adjusting the power level of a light source.
The ability of beamsplitters to split and recombine light, control its intensity, and generate interference patterns makes them invaluable tools for optical engineers and scientists. Their cost-effectiveness and ease of use ensure they remain a mainstay in the toolkit of those working in the field. So the next time you marvel at the precision of an interferometer, the insights from a spectrometer, or the intricacies revealed by a microscope, remember that beamsplitters play a significant role in making it all possible.